Authors identify capsaicin receptor TRPV1 as a key regulator of Ca2+ entry into axoplasm that is required for developmental degeneration modeled by NGF withdrawal from sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion in vitro.
Authors found that experimentally induced stroke causes a secondary wave of brain tissue inflammation that shares some molecular and morphological characteristics with atherosclerosis.
Authors describe an unexpected effect of in utero electroporation of plasmid DNA on the distribution of microglia within the developing forebrain.
Dr. Jacqueline Barker tells the story about her first-author eNeuro paper that showed that action-outcome relationships are differentially encoded by the infralimbic prefrontal cortex during goal-directed and habitual behaviors.
Check out the top 10 most downloaded articles published in eNeuro in 2018.
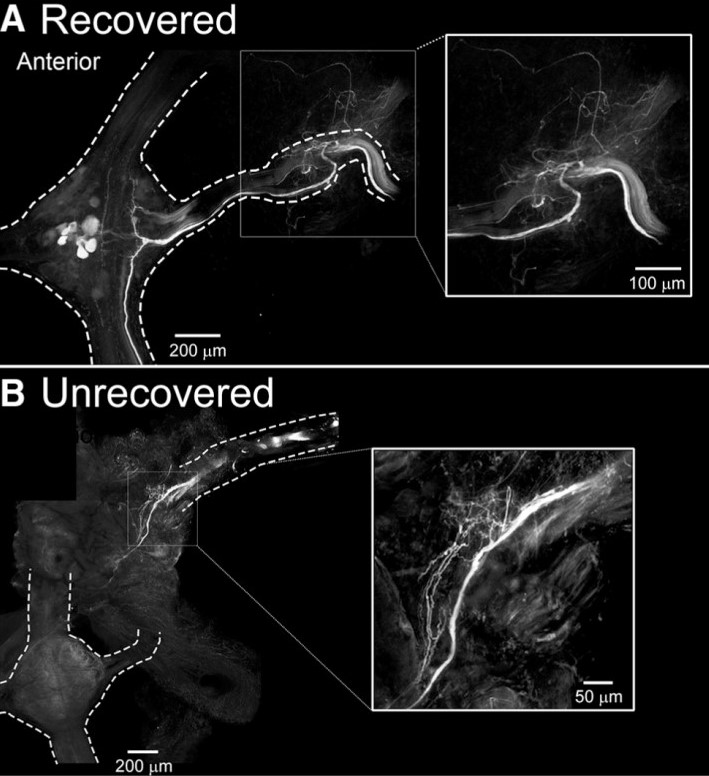
Authors demonstrate that in the absence of descending cephalic input, locomotor recovery in the leech is achieved by a switch to dependence on afferent information from peripheral nerves in the body wall.
Authors addressed the question 'what, if anything, is rodent prefrontal cortex?' by carrying out a survey of prefrontal cortex researchers and uncovered points of agreement as well as differences in regard to what brain areas constitute "prefrontal cortex" in rodents."
Authors show that axons of inhibitory neurons have distinctive structural and molecular features that contrast with those of the majority of myelinated excitatory axons in human neocortex.
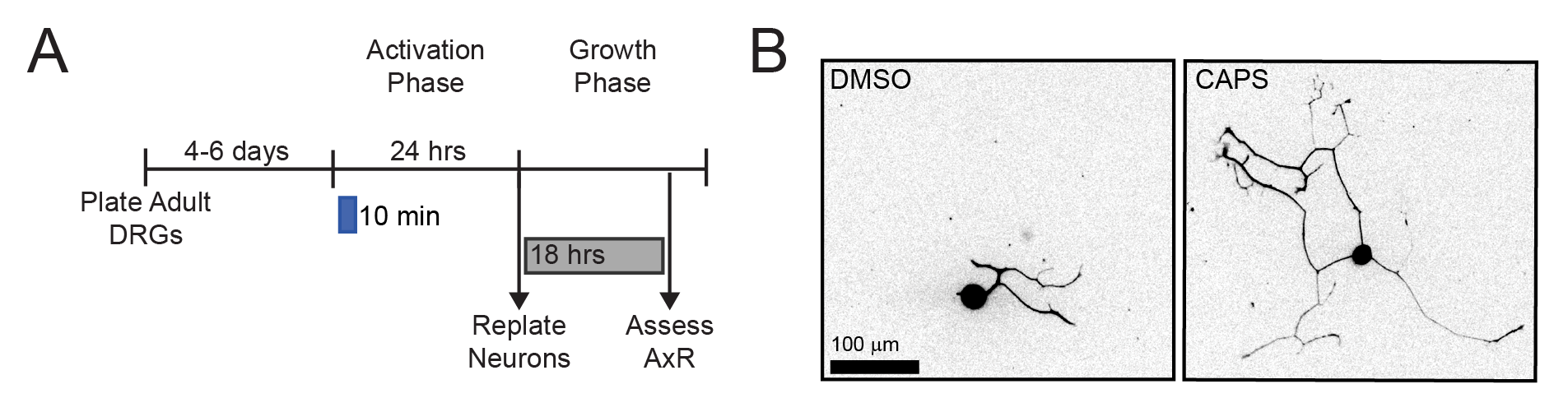
Authors demonstrate that capsaicin, a TRPV1 agonist, activates a pro-axon growth program, suggesting an approach for enhancing axon regeneration in selective populations of neurons.
Authors functionally defined immediate-early astrocytes (ieAstrocytes) as an in vivo astrocyte population, modulated by S1P signaling, in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.
FOLLOW US
TAGS
CATEGORIES
POPULAR POSTS
- Editor’s Pick: Bridging the translational gap to improve our understanding of OCD
- Beyond the Paper: A Conversation with Dr. Krishnakanth Kondabolu and Dr. Natalie Doig
- Snapshots in Neuroscience: In vivo and ex vivo cross-section images of tree shrew retinas
- Beyond the Paper: A Conversation with Dr. Naoki Shigematsu


.jpg)
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed




